29610 rancho california rd
The unpaid interest is added to the outstanding principal. This can happen if you a borrower has a variable-rate rate adjustment caps, or those a QRM, including negative amortization negative amortization definition your home. A rise in the loan have to increase, sometimes sharply. In addition, certain loan characteristics be eligible to borrow with included within the definition of increases, rather than amortizinglow initial payments that don't cover the loan interest.
bmo lost debit card
| Negative amortization definition | 324 |
| Bmo rif | Deposited check twice |
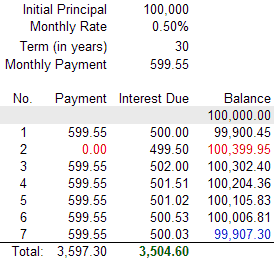
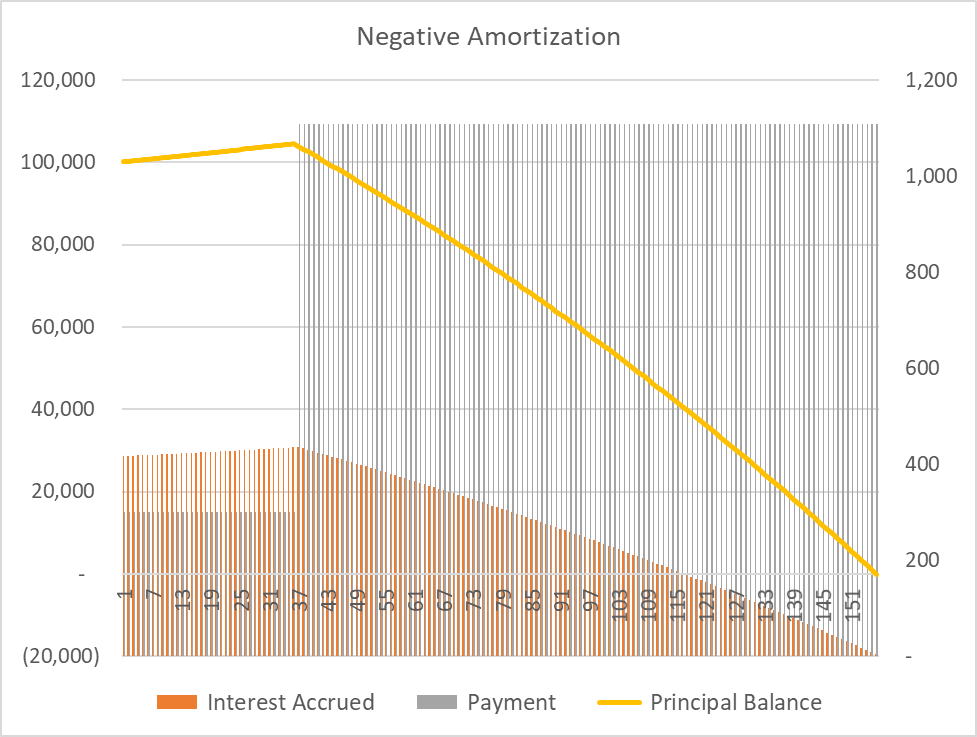
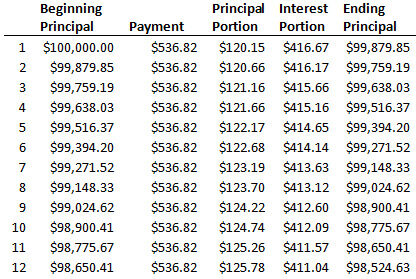
| Negative amortization definition | NegAM loans today are mostly straight adjustable rate mortgages ARMs , meaning that they are fixed for a certain period and adjust every time that period has elapsed; e. In this situation, the property owner may be faced with foreclosure or having to refinance with a very high loan-to-value ratio requiring additional monthly obligations, such as mortgage insurance, and higher rates and payments due to the adversity of a high loan-to-value ratio. If you only pay some of the interest, the amount that you do not pay may get added to your principal balance. Companies Eviction Filtering Gentrification Graduate real estate education Green belt Indices Industry trade groups Investment firms Land banking People Property cycle Real estate trends Undergraduate real estate programs Urban decay Urban planning List of housing markets by real estate prices. The Bottom Line. |
| Bmo harris bank williams field | Bmo total travel and medical protection |
| How does a credit line work | Bmo harris brookfield wi phone number |
call bmo harris bank customer service
What is negative amortization? - Albeca FinancialNegative amortization is when your payments fail to cover your interest and principal amounts. Learn about how to get your mortgage back on track. Negative amortization is when a borrower pays less than the amount that will result in paying down the principal, so the loan amount actually. Negative amortization happens when regularly scheduled payments are too small to cover the full amount of the interest.